No products in the cart.
New Laboratory Equipment, Fermentation
Decoding GMP in the World of Fermentation
Introduction
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) are essential guidelines and regulations that ensure the quality, safety, and consistency of pharmaceuticals, food products, and other goods manufactured for human consumption. These regulations are not limited to the final product but extend to every manufacturing process step, including fermentation. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of GMP in fermentation, why it is crucial, and how it impacts the production of various valuable products.
What is GMP?
GMP, or Good Manufacturing Practices, is a set of quality assurance standards and guidelines that ensure that products are consistently produced and controlled to meet the quality standards appropriate for their intended use. These standards apply to various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food, biotechnology, and fermentation.
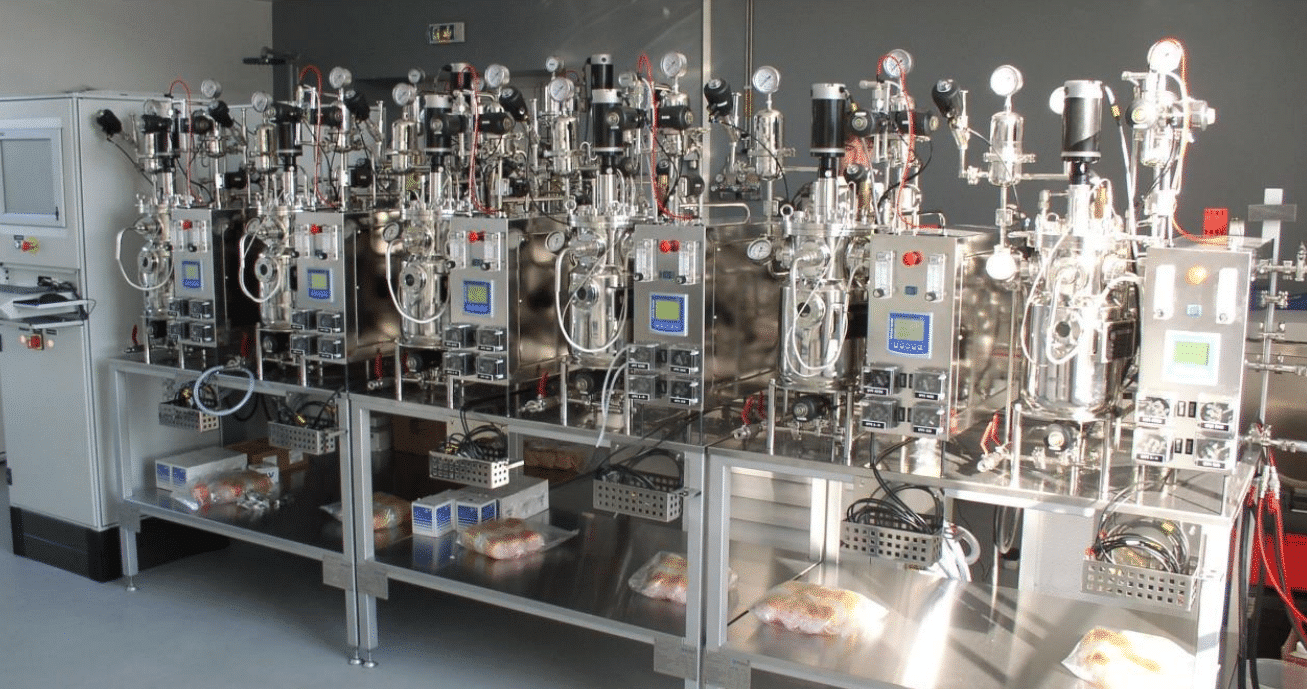
shop gmi fermenters & bioreactorsThe Role of GMP in Fermentation
Fermentation plays a pivotal role in various industries, including the production of pharmaceuticals, biofuels, enzymes, and specialty chemicals. Ensuring that the fermentation process adheres to GMP is crucial for the following reasons:
- Quality Control: GMP ensures that every step of the fermentation process is well-documented and controlled. This includes monitoring environmental conditions, such as temperature, pH, and oxygen levels, as well as the quality of raw materials, microbial strains, and equipment used in the process.
- Consistency: GMP guidelines help maintain the consistency and reproducibility of fermentation processes. This is especially important in industries like pharmaceuticals, where minor variations can impact the efficacy and safety of the final product.
- Product Safety: GMP standards help ensure the safety of the final product. This is particularly critical in the food and pharmaceutical industries, where contaminated or impure products can pose serious health risks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries are subject to strict regulatory oversight, and compliance with GMP is often a legal requirement. Failure to adhere to these guidelines can lead to product recalls, fines, and legal consequences.
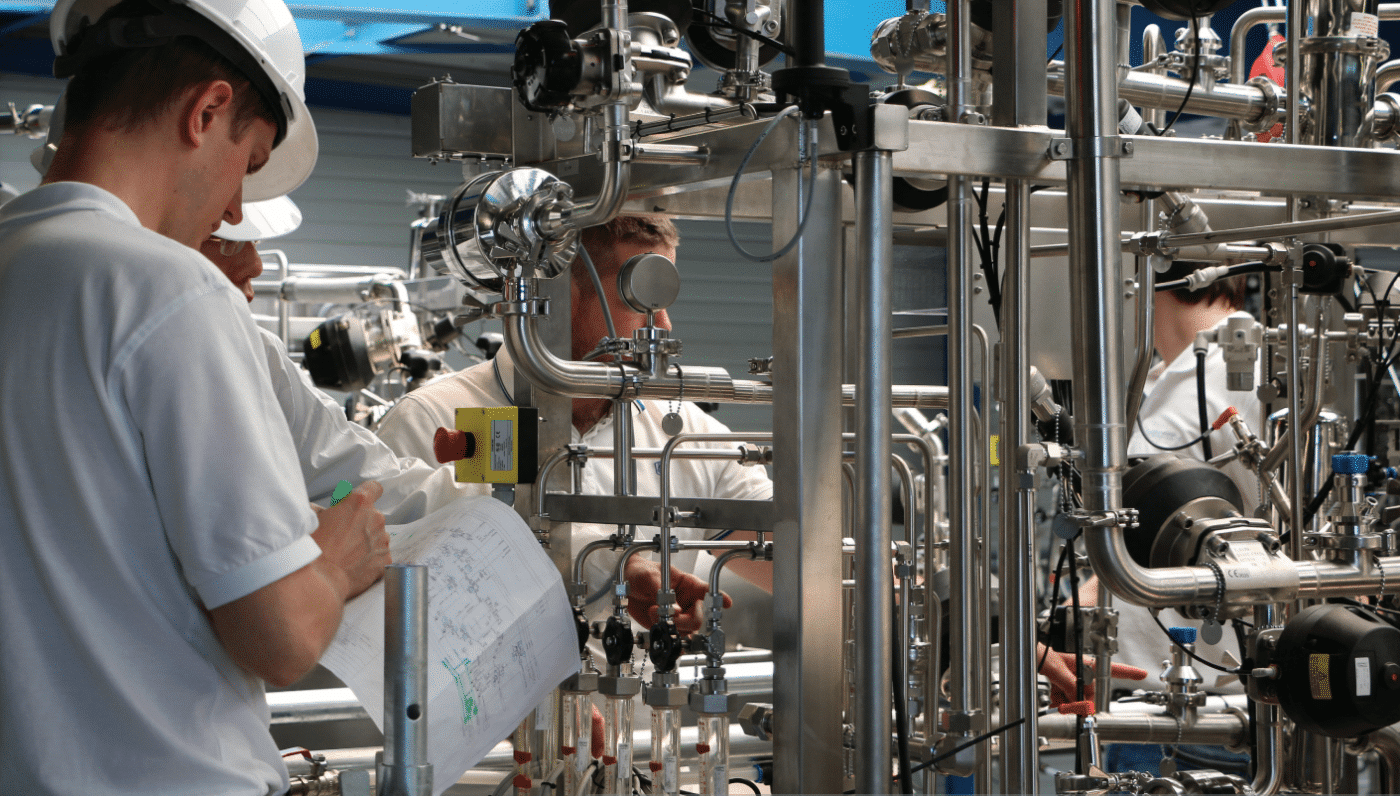

GPC – Innovative Bioreactors
- Made in France
- Exclusively available at GMI
- Completely Customizable, Cost-efficient, Intuitive Software
Key Elements of GMP in Fermentation
To maintain GMP in fermentation, several key elements must be observed:
- Facility Design and Maintenance: Facilities must be designed to prevent contamination and maintain optimal environmental conditions. This includes air filtration, cleanrooms, and proper waste disposal.
- Equipment and Instrumentation: Equipment used in fermentation must be appropriately maintained and calibrated to ensure accuracy and reliability. Regular validation and qualification of equipment are necessary.
- Process Documentation: All aspects of the fermentation process, from raw material sourcing to microbial culture preparation, must be well-documented. Standard operating procedures (SOPs) play a vital role in ensuring consistency.
- Personnel Training: Personnel involved in fermentation should be well-trained and adhere to proper hygiene and safety protocols. This includes thorough training in GMP procedures and compliance.
- Quality Control and Testing: Quality control procedures, including in-process and final product testing, are essential to ensure product quality. Depending on the industry, this might involve microbial testing, purity analysis, and potency testing.
- Documentation and Record Keeping: Proper record-keeping is a fundamental aspect of GMP. All data related to the fermentation process, including deviations and corrective actions, should be documented and maintained.
Conclusion
Decoding GMP in fermentation is essential for ensuring product quality, safety, and consistency in industries where fermentation is a critical step in production. GMP guidelines provide the framework to achieve these objectives by controlling environmental conditions, equipment, processes, and personnel. Compliance with GMP helps meet regulatory requirements and safeguards the reputation and success of industries relying on fermentation to produce vital goods. It’s a crucial component of responsible manufacturing in today’s world.